Demystifying Data Mapping Challenges: Recommendations and Best Practices
In part one of my post about data mapping, I explored the importance of data mapping and its strategic implications for corporations. In part two, as promised, I will delve into the common challenges faced during the data mapping process and provide practical recommendations and best practices to overcome them. By implementing these strategies, you can aim for a smooth and successful data mapping journey, unlocking the full potential of data assets.
[My Information Master’s Practicum working with a provincial open data program sparked the thoughts in the creation of this post.]
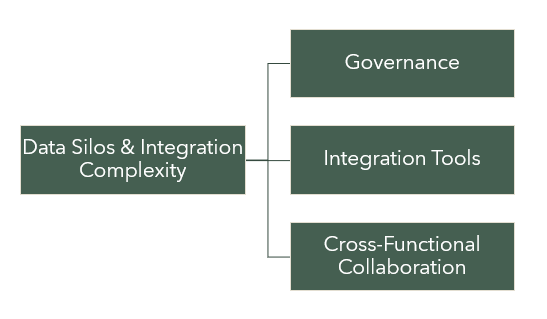
Data Silos and Integration Complexity:
Challenge: Data silos, where data is fragmented and isolated across different systems or departments, pose a significant obstacle to effective data mapping. Additionally, integrating data from diverse sources can be complex and time-consuming.
Recommendations:
a. Establish a Data Governance Framework: Implement a data governance framework that defines data ownership, standards, and policies across the organization. This framework encourages collaboration, data sharing, and a unified approach to data management.
b. Invest in Data Integration Tools: Leverage modern data integration tools that simplify the process of connecting and consolidating data from various sources. These tools streamline the integration process, automate data pipelines, and ensure data consistency and quality.
c. Promote Cross-Functional Collaboration: Foster collaboration between different teams and departments involved in data mapping initiatives. Encourage open communication, knowledge sharing, and joint problem-solving to break down data silos and facilitate seamless integration.
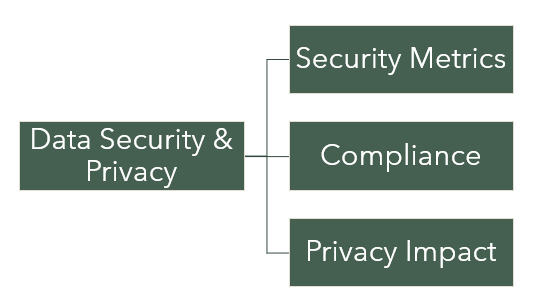
Data Security and Privacy:
Challenge: Safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations are paramount concerns when working with data mapping initiatives.
Recommendations:
a. Implement Robust Data Security Measures: Establish strict access controls, encryption protocols, and monitoring systems to protect data integrity and confidentiality. Regularly audit and update security measures to stay ahead of evolving threats.
b. Comply with Data Privacy Regulations: Stay informed about data privacy regulations relevant to your industry and region, such as GDPR or CCPA. Adhere to compliance requirements by obtaining necessary consent, anonymizing data when needed, and ensuring data usage aligns with legal guidelines.
c. Conduct Privacy Impact Assessments: Prioritize privacy impact assessments to identify and mitigate potential risks associated with data mapping activities. These assessments evaluate the impact of data collection, storage, and sharing on individual privacy and help ensure ethical and responsible data handling practices.
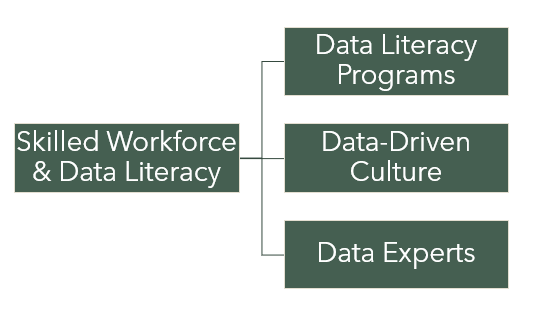
Skilled Workforce and Data Literacy:
Challenge: Nurturing a skilled workforce capable of handling data mapping processes and making strategic use of data can be a significant challenge.
Recommendations:
a. Invest in Data Literacy Programs: Develop data literacy programs to enhance employees’ understanding of data concepts, analytics tools, and data-driven decision-making. Provide training sessions, workshops, and resources to empower the workforce with the necessary skills.
b. Foster a Data-Driven Culture: Encourage a culture that values data and promotes its strategic use. Foster curiosity, experimentation, and innovation, and recognize and reward data-driven initiatives. This cultural shift will motivate employees to embrace data mapping practices and leverage data for strategic insights.
c. Collaborate with Data Experts: Engage data experts such as data scientists, analysts, or consultants to support data mapping initiatives. Their expertise can provide guidance, address complex challenges, and help implement best practices effectively.
Overcoming data mapping challenges requires a strategic and holistic approach. By implementing the recommendations and best practices outlined above, organizations can navigate data silos, ensure data security and privacy, and cultivate a skilled workforce. Embrace these practices to unlock the true potential of data mapping and drive data-informed decision-making across your corporation.
Remember, data mapping is an iterative process. Continuously evaluate and adapt your strategies to align with evolving business needs, technological advancements, and regulatory requirements. By doing so, you can stay at the forefront of data-driven innovation and gain a competitive edge in the digital landscape.
Stay tuned for part three on this topic, where I will explore real-world case studies highlighting the transformative impact of effective data mapping practices.

0 Comments